COLOP(range_array, operation)
Applies 2nd argument, operation, to the matrix column-wise resulting in a single column-vector.
Range_array can take the form of an explicit cell range (such as A1:C3) or the name of a named range.
Operation may be:
- ‘+’ or ‘sum’ (addition),
- '*' or ‘prod’ (product),
- ‘ave’ (average),
- ‘max’ (maximum)
- ‘min’ (minimum)
- 'and'
- 'or'
Examples
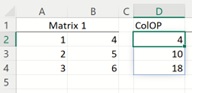
Example 1: Matrix 1 is shown below; each element is a constant.
See the COLOP function in cell D2 = COLOP(A2:B4, “*”)
D2 = A2 * B2 = 1 * 4 = 4
D3 = A3 * B3 = 2 * 5 = 10
D4 = A4 * B4 = 3 * 6 = 18
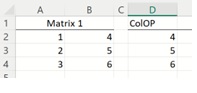
Example 2: Matrix 1 is shown below; each element is a constant.
See the COLOP function in cell D2 = COLOP(A2:B4, “max”)
D2 = MAX(A2, B2) = MAX(1,4) = 4
D3 = MAX(A3, B3) = MAX(2,5) = 5
D4 = MAX(A4, B4) = MAX(3,6) = 6
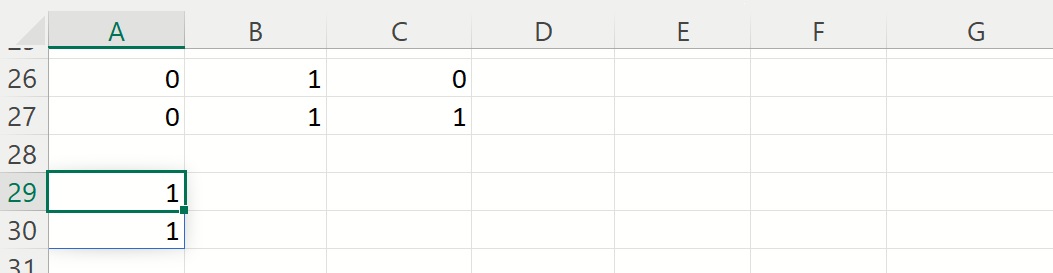
Example 3: Given a matrix containing binary values. The formula =COLOP(A26:C27, “or”) returns a 1 in cells A29 and A30 to indicate that there is at least one “1” in the ranges, A26:C26 and A27:C27.